Speed Up Your PC Using Run Commands
Is your PC running slower than usual? Speeding up your computer doesn't always require advanced tools or software. With a few simple Run commands, you can optimize your system's performance and make it run smoother and faster.
In this guide, you'll learn how to use the Run Command to:
- ⭕ Clean up temporary files and cache to free up disk space
- ⭕ Manage startup programs to reduce boot time
- ⭕ Defragment your hard drive for better file access speeds
- ⭕ Check and repair system files to ensure your PC is running optimally
- ⭕ Adjust system settings for improved performance
Follow these easy steps and discover how you can give your PC a noticeable boost in speed and efficiency using just the Run Command. Perfect for both beginners and advanced users looking to maintain a fast and responsive computer.
Clear Temporary Files

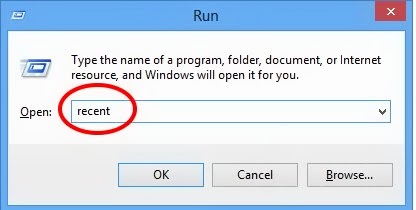
Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, then type recent, temp, %temp%, and prefetch one by one, pressing Enter after each. Delete all files in these folders. These folders contain temporary files that can slow down your computer if they accumulate. It is safe to delete these files as they are no longer needed by your system.
Disk Cleanup
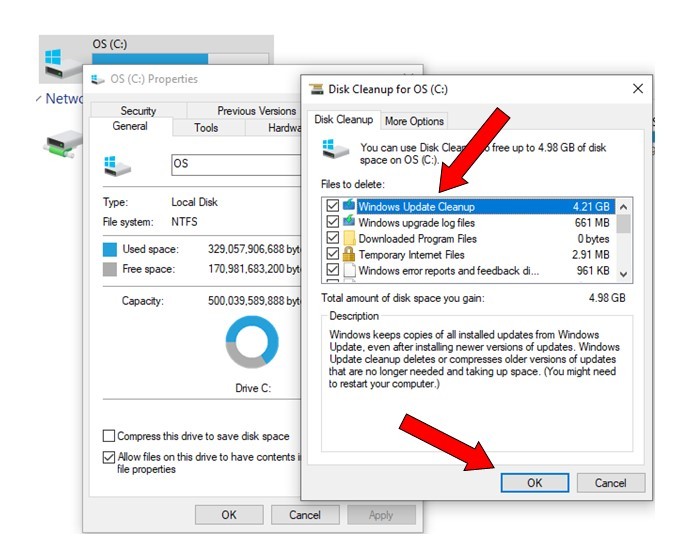
Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, type cleanmgr, and press Enter. Select the drive you want to clean up, and click OK. Disk Cleanup will scan the drive for unnecessary files that you can delete to free up space. This includes temporary files, system files, and items in the Recycle Bin. Once the scan is complete, check the boxes next to the types of files you want to delete and click OK to remove them.
Defragment and Optimize Drives


Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, type dfrgui, and press Enter. Select the drive you want to defragment and click on Optimize. Defragmentation reorganizes the data on your hard drive so that related pieces of data are put back together, which can improve access speed. This process is particularly useful for mechanical hard drives but is generally not necessary for SSDs.
Manage Startup Programs
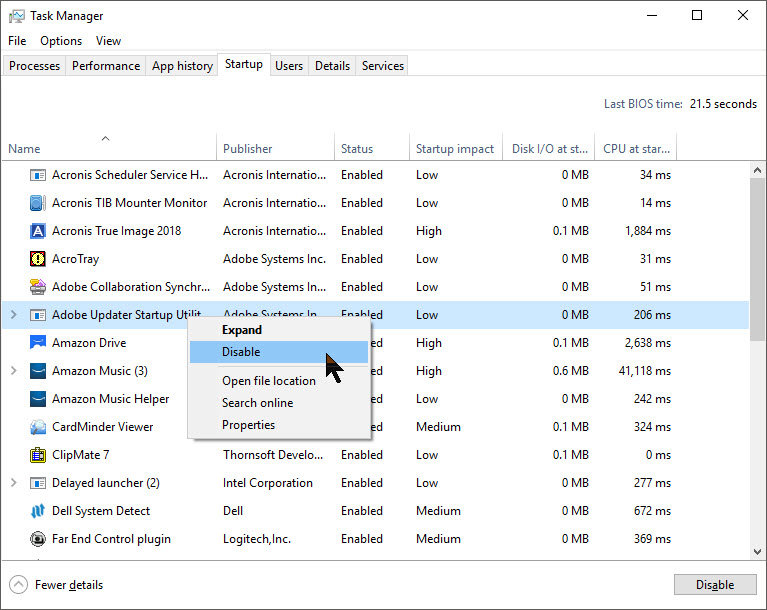
Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, type taskmgr, and press Enter. Go to the Startup tab, and disable any programs you don't need to start automatically with Windows. Many programs set themselves to start when Windows starts, which can slow down your boot time and consume system resources. Only disable programs that you recognize and don't need to run at startup.
Check for Disk Errors


Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, type chkdsk /f, and press Enter. This will schedule a disk check on the next restart. Checking for disk errors can help identify and fix file system errors and bad sectors on your hard drive, which can cause slowdowns and data loss. You may be prompted to restart your computer to allow the disk check to run.
System File Checker


Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, type cmd, and press Enter. Type sfc /scannow and press Enter. This command will scan and repair any corrupted system files. System File Checker is a utility that helps fix problems with Windows system files. If it finds any issues, it will attempt to replace the corrupted files with a cached copy that is stored in a compressed folder at %WinDir%\System32\dllcache.
Adjust Appearance and Performance of Windows


Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, type sysdm.cpl, and press Enter. Go to the Advanced tab, click on Settings under Performance, and choose Adjust for best performance or customize the visual effects. Disabling some of the visual effects can make your PC run faster, especially on older hardware. You can also select Custom to pick and choose which effects to disable.
Remove Unnecessary Programs


Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, type appwiz.cpl, and press Enter. This opens the Programs and Features window. Uninstall programs that you no longer need. Removing unused programs can free up system resources and disk space. Be careful not to remove any programs that you might need or that are required for your system's functionality.
Disable Unnecessary Services


Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, type services.msc, and press Enter. This opens the Services window. Scroll through the list and disable services you don't need by right-clicking them and selecting Properties, then changing the Startup type to Disabled. Disabling unnecessary services can free up system resources. However, be cautious and only disable services that you are sure you do not need.
Increase Virtual Memory


Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, type sysdm.cpl, and press Enter. Go to the Advanced tab, click on Settings under Performance, then go to the Advanced tab again, and click on Change under Virtual memory. Adjust the settings to increase the paging file size. Virtual memory can help your system handle larger workloads by using a portion of your hard drive as additional RAM. Ensure that you set a size that is 1.5 to 2 times the amount of your physical RAM.
Update Drivers


Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, type devmgmt.msc, and press Enter. This opens Device Manager. Right-click on each device and select Update driver to ensure all drivers are up to date. Keeping your drivers up to date can improve performance and fix compatibility issues. Be sure to get your drivers from a reputable source, such as the device manufacturer's website or Windows Update.
Check for Malware


Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box, type mrt, and press Enter. This opens the Microsoft Windows Malicious Software Removal Tool. Run a full scan to check for malware. Malware can significantly slow down your computer and cause other issues. It is important to regularly scan your system and ensure it is protected with up-to-date antivirus software.
Reduce Boot Timeout


Press Win + R, type msconfig, and press Enter. Go to the Boot tab and reduce the Timeout value.




 iP Address Movie
iP Address Movie Text Style
Text Style Fun Time
Fun Time Bangla Text to Speech
Bangla Text to Speech Masters Results
Masters Results


0 Comments